Is lack of sleep affecting your performance?
Lack of sleep affects your judgment, coordination, and reaction times. In fact, sleep deprivation can affect you just as much as being drunk. The BBC has a fun test to help you determine if lack of sleep is affecting your performance.
Try the Sheep Dash test and see how well rested you really are.
How Much Sleep Do You Need?
SLEEP CYCLES & STAGES, LACK OF SLEEP, AND GETTING THE HOURS YOU NEED
When you’re scrambling to meet the demands of modern life, cutting back on sleep can seem like the only answer. How else are you going to get through your neverending to-do list or make time for a little fun? Sure, a solid eight hours sounds great, but who can afford to spend so much time sleeping? The truth is you can’t afford not to.
Sleep consists of a series of distinct cycles and stages that restore and refresh your body and mind. Even minimal sleep loss takes a toll on your mood, energy, efficiency, and ability to handle stress. If you want to feel your best, stay healthy, and perform up to your potential, sleep is a necessity, not a luxury. Learn what happens when you’re sleeping, how to determine your nightly sleep needs, and what you can do to bounce back from chronic sleep loss and get on a healthy sleep schedule.
The power of sleep
Many of us want to sleep as little as possible—or feel like we have to. There are so many things that seem more interesting or important than getting a few more hours of sleep. But just as exercise and nutrition are essential for optimal health and happiness, so is sleep. The quality of your sleep directly affects the quality of your waking life, including your mental sharpness, productivity, emotional balance, creativity, physical vitality, and even your weight. No other activity delivers so many benefits with so little effort!
Understanding sleep
Sleep isn’t merely a time when your body and brain shut off. While you rest, your brain stays busy, overseeing a wide variety of biological maintenance tasks that keep you running in top condition and prepare you for the day ahead. Without enough hours of restorative sleep, you’re like a car in need of an oil change. You won’t be able to work, learn, create, and communicate at a level even close to your true potential. Regularly skimp on “service” and you’re headed for a major mental and physical breakdown.
The good news is that you don’t have to choose between health and productivity. As you start getting the sleep you need, your energy and efficiency will go up. In fact, you’re likely to find that you actually get more done during the day than when you were skimping on shuteye.
Myths and Facts about Sleep
Myth 1: Getting just 1 hour less sleep per night won’t effect your daytime functioning. You may not be noticeably sleepy during the day. But even slightly less sleep can affect your ability to think properly and respond quickly, and compromise your cardiovascular health, energy balance, and ability to fight infections.
Myth 2: Your body adjusts quickly to different sleep schedules. Most people can reset their biological clock, but only by appropriately timed cues—and even then, by 1–2 hours per day at best. Consequently, it can take more than a week to adjust after traveling across several time zones or switching to the night shift.
Myth 3: Extra sleep at night can cure you of problems with excessive daytime fatigue. Not only is the quantity of sleep important but also the quality of sleep. Some people sleep 8 or 9 hours a night but don’t feel well rested when they wake up because the quality of their sleep is poor.
Myth 4: You can make up for lost sleep during the week by sleeping more on the weekends. Although this sleeping pattern will help relieve part of a sleep debt, it will not completely make up for the lack of sleep. Furthermore, sleeping later on the weekends can affect your biological clock so that it is much harder to go to sleep at the right time on Sunday nights and get up early on Monday mornings.
Adapted from Your Guide to Healthy Sleep (PDF) – The National Institutes of Health
How many hours of sleep do you need?
|
Average Sleep Needs |
|
|
Age |
Hours |
| Newborns (0-2 months) | 12 – 18 |
| Infants (3 months to 1 year) | 14 – 15 |
| Toddlers (1 to 3 years) | 12 – 14 |
| Preschoolers (3 to 5 years) | 11 – 13 |
| School-aged children (5 to 12 years) | 10 – 11 |
| Teens and preteens (12 to 18 years) | 8.5 – 10 |
| Adults (18+) | 7.5 – 9 |
According to the National Institutes of Health, the average adult sleeps less than 7 hours per night. In today’s fast-paced society, 6 or 7 hours of sleep may sound pretty good. In reality, it’s a recipe for chronic sleep deprivation.
While sleep requirements vary slightly from person to person, most healthy adults need between 7.5 to 9 hours of sleep per night to function at their best. Children and teens need even more (see box at right). And despite the notion that sleep needs decrease with age, older people still need at least 7.5 to 8 hours of sleep. Since older adults often have trouble sleeping this long at night, daytime naps can help fill in the gap.
Sleep needs and peak performance
There is a big difference between the amount of sleep you can get by on and the amount you need to function optimally. Just because you’re able to operate on 7 hours of sleep doesn’t mean you wouldn’t feel a lot better and get more done if you spent an extra hour or two in bed. The best way to figure out if you’re meeting your sleep needs is to evaluate how you feel as you go about your day. If you’re logging enough hours, you’ll feel energetic and alert all day long, from the moment you wake up until your regular bedtime.
Think six hours of sleep is enough?
Think again. Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco discovered that some people have a gene that enables them to do well on 6 hours of sleep a night. But the gene is very rare, appearing in less than 3% of the population. For the other 97% of us, six hours doesn’t come close to cutting it.
You may be sleep deprived if you…
■ Need an alarm clock in order to wake up on time
■ Rely on the snooze button
■ Have a hard time getting out of bed in the morning
■ Feel sluggish in the afternoon
■ Get sleepy in meetings, lectures, or warm rooms
■ Get drowsy after heavy meals or when driving
■ Need to nap to get through the day
■ Fall asleep while watching TV or relaxing in the evening
■ Feel the need to sleep in on weekends
■ Fall asleep within five minutes of going to bed
While it may seem like losing sleep isn’t such a big deal, sleep deprivation has a wide range of negative effects that go way beyond daytime drowsiness.
The effects of sleep deprivation and chronic lack of sleep
■ Fatigue, lethargy, and lack of motivation
■ Moodiness and irritability
■ Reduced creativity and problem-solving skills
■ Inability to cope with stress
■ Reduced immunity; frequent colds and infections
■ Concentration and memory problems
■ Weight gain
■ Impaired motor skills and increased risk of accidents
■ Difficulty making decisions
■ Increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other health problems
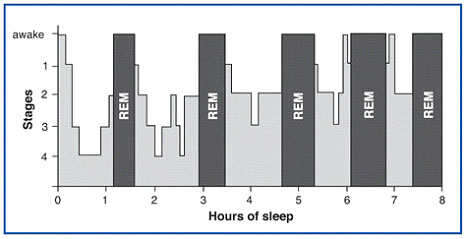
Stages of sleep: REM sleep and non-REM sleep stages
All sleep is not created equal. Sleep unfolds in a series of recurring sleep stages that are very different from one another in terms of what’s happening beneath the surface. From deep sleep to dreaming sleep, they are all vital for your body and mind. Each stage of sleep plays a different part in preparing you for the day ahead.
There are two main types of sleep:
■ Non-REM (NREM) sleep consists of four stages of sleep, each deeper than the last.
■ REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is when you do most active dreaming. Your eyes actually move back and forth during this stage, which is why it is called Rapid Eye Movement sleep.
|
The Stages of Sleep |
|
Non-REM sleep |
| Stage 1 (Transition to sleep) – Stage 1 lasts about five minutes. Eyes move slowly under the eyelids, muscle activity slows down, and you are easily awakened. |
| Stage 2 (Light sleep) – This is the first stage of true sleep, lasting from 10 to 25 minutes. Eye movement stops, heart rate slows, and body temperature decreases. |
| Stage 3 (Deep sleep) – You’re difficult to awaken, and if you are awakened, you do not adjust immediately and often feel groggy and disoriented for several minutes. |
| Stage 4 (More intense deep sleep) – The deepest stage of sleep. Brain waves are extremely slow. Blood flow is directed away from the brain and towards the muscles, restoring physical energy. |
|
REM sleep |
| REM sleep (Dream sleep) – About 70 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, you enter REM sleep, where dreaming occurs. Eyes move rapidly. Breathing is shallow. Heart rate and blood pressure increase. Arm and leg muscles are paralyzed. |
The sleep cycle: Understanding the architecture of sleep
You may think that once you go to bed, you soon fall into a deep sleep that lasts for most of the night, progressing back into light sleep in the morning when it’s time to wake up. In reality, the sleep cycle is a lot more complicated.
When you chart the sleep stages over the course of the night, the result looks like a city skyline—which is why it is called “sleep architecture”
During the night, your sleep follows a predictable pattern, moving back and forth between deep restorative sleep (deep sleep) and more alert stages and dreaming (REM sleep). Together, the stages of REM and non-REM sleep form a complete sleep cycle that repeats until you wake up.
The amount of time you spend in each stage of sleep changes as the night progresses. For example, most deep sleep occurs in the first half of the night. Later in the night, your REM sleep stages become longer, alternating with light Stage 2 sleep. This is why if you are sensitive to waking up in the middle of the night, it is probably in the early morning hours, not immediately after going to bed.
Having a hard time getting up? Take advantage of the 90-minute sleep cycle.
Even if you’ve enjoyed a full night’s sleep, getting out of bed isn’t easy if your alarm goes off when you’re in the middle of the deeper stages of sleep (especially stages 3 and 4). If you want to make mornings less painful, set a wake-up time that’s a multiple of 90 minutes, the length of the average sleep cycle. For example, if you go to bed at 10 p.m., set your alarm for 5:30 (a total of 7 ½ hours of sleep) instead of 6:00 or 6:30. You’ll feel more refreshed at 5:30 than you will with another 30 to 60 minutes of sleep, because you’re getting up when your body and brain are already close to wakefulness.
The importance of deep sleep and REM sleep
Getting good, restorative sleep is not just a matter of spending enough hours in bed. The amount of time you spend in each of the stages of sleep matters. A normal adult spends approximately 50 percent of total sleep time in stage 2 sleep, 20 percent in REM sleep, and 30 percent in the remaining stages, including deep sleep.
Each stage of sleep in the sleep cycle offers benefits to the sleeper. However, deep sleep (stages 3 and 4) and REM sleep are particularly important.
Deep sleep
The most damaging effects of sleep deprivation are from inadequate deep sleep. Deep sleep is a time when the body repairs itself and builds up energy for the day ahead. It plays a major role in maintaining your health, stimulating growth and development, repairing muscles and tissues, and boosting your immune system. In order to wake up energized and refreshed, getting quality deep sleep is key. Factors that can lead to poor or inadequate deep sleep include:
■ Being woken during the night (by outside noise, for example, or in order to care for a crying baby)
■ Working night shifts or swing shifts. Getting quality deep sleep during the day can be difficult, due to light and excess noise.
■ Smoking or drinking in the evening. Substances like alcohol and nicotine can disrupt deep sleep. It’s best to limit them before bed.
REM sleep
Just as deep sleep renews the body, REM sleep renews the mind. REM sleep plays a key role in learning and memory. During REM sleep, your brain consolidates and processes the information you’ve learned during the day, forms neural connections that strengthen memory, and replenishes its supply of neurotransmitters, including feel-good chemicals such as serotonin and dopamine that boost your mood during the day.
To get more mind and mood-boosting REM sleep, try sleeping an extra 30 minutes to an hour in the morning, when REM sleep stages are longer. Improving your overall sleep will also increase your REM sleep. If you aren’t getting enough deep sleep, your body will try to make it up first, at the expense of REM sleep.
Tips for getting good sleep, night after night
Do you feel like no matter how much you sleep, you still wake up exhausted? Learn how to maximize your sleep quality and sleep well every night by following a regular sleep-wake schedule, developing a relaxing bedtime routine, and improving your sleep environment.
Read: Tips for Getting Better Sleep: How to Sleep Well Every Night
Paying off your sleep debt
Sleep debt is the difference between the amount of sleep you need and the hours you actually get. Every time you sacrifice on sleep, you add to the debt. Eventually, the debt will have to be repaid. It won’t go away on its own. If you lose an hour of sleep, you must make up that extra hour somewhere down the line in order to bring your “account” back into balance.
Sleeping in on the weekends isn’t enough!
Many of us try to repay our sleep debt by sleeping in on the weekends. But as it turns out, bouncing back from chronic lack of sleep isn’t that easy. One or two solid nights of sleep aren’t enough to pay off a long-term debt. While extra sleep can give you a temporary boost (for example, you may feel great on Monday morning after a relaxing weekend), your performance and energy will drop back down as the day wears on.
Tips for getting and staying out of sleep debt
While you can’t pay off sleep debt in a night or even a weekend, with a little effort and planning, you can get back on track.
■ Aim for at least 8 hours of sleep every night. Make sure you don’t fall farther in debt by blocking off a minimum of 8 hours for sleep each night. Consistency is the key.
■ Settle short-term sleep debt with an extra hour or two per night. If you lost 10 hours of sleep, pay the debt back in nightly one or two-hour installments.
■ Keep a sleep diary. Record when you go to bed, when you get up, your total hours of sleep, and how you feel during the day. As you keep track of your sleep, you’ll discover your natural patterns and get to know your sleep needs. Click here to download Helpguide’s sleep diary.
■ Take a sleep vacation to pay off a long-term sleep debt. Pick a two-week period when you have a flexible schedule. Go to bed at the same time every night and allow yourself to sleep until you wake up naturally. No alarm clocks! If you continue to keep the same bedtime and wake up naturally, you’ll eventually dig your way out of debt and arrive at the sleep schedule that’s ideal for you.
■ Make sleep a priority. Just as you schedule time for work and other commitments, you should schedule enough time for sleep. Instead of cutting back on sleep in order to tackle the rest of your daily tasks, put sleep at the top of your to-do list.
Related links for sleep cycles, stages, hours, and needs
Understanding sleep
Brain Basics: Understanding Sleep – Learn about sleep benefits and sleep needs, dreaming, circadian rhythms, sleep cycles and stages, and sleep disorders. (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke)
Your Guide to Healthy Sleep (PDF) – Comprehensive guide to sleep and why it matters. Learn about the stages and cycles of sleep, the dangers of sleep deprivation, and dealing with common sleep problems. (National Institutes of Health)
Sleep needs
Assess Your Sleep Needs – Learn about typical sleep needs and how to determine your own nightly needs. (Get Sleep, Harvard Medical School Division of Sleep Medicine)
How Much Sleep Do We Really Need? – Research on sleep needs and sample sleep requirements in different age ranges. (The National Sleep Foundation)
How Much Sleep Is Enough for My Child? – Figure out if your child is getting adequate sleep and learn about the sleep needs of different age groups. (KidsHealth)
Sleep deprivation and sleep debt
Effects of Sleep Deprivation – Learn about the consequences of sleep deprivation and how you can pay off your sleep debt. (Stanford Sleep & Dreams)
Consequences of Insufficient Sleep – Series of articles and videos on the consequences of sleep deprivation and chronic lack of sleep, including its impact on driving, judgment, and disease risk. (Healthy Sleep Web Site)
Can You Catch Up on Lost Sleep? – Explore the consequences of sleep debt, including its effects on health, productivity, and performance. Includes tips on how to repay sleep debt. (Scientific American)